Systems analysis of coastal aquifers
Theme leader: Prof. Pieter Stuyfzand
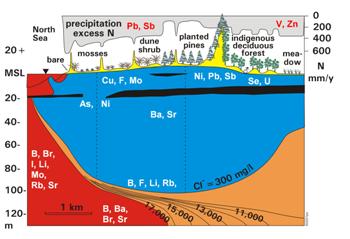
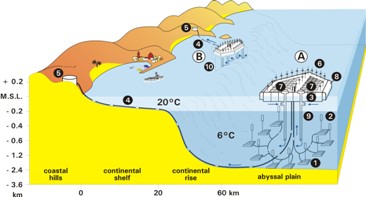
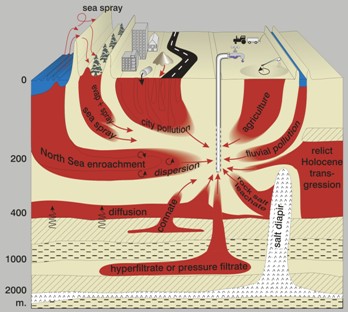
Coastal aquifers are highly complex systems due to: (a) small scale variations in lithology, surface-groundwater interactions and water density; (b) added dynamism because of fluctuations in sea level, coastline position and river discharge; and (c) multiple anthropogenic impacts.
Due to their location in often densely populated areas, coastal aquifers tend to be particularly data-rich. Their groundwater typically shows a broad spectrum in terms of origin, salinity, alkalinity, redox potential, extent of ion exchange and degree of pollution.
Managed aquifer recharge is often applied to reduce salinization risks and to store surface water for later use.
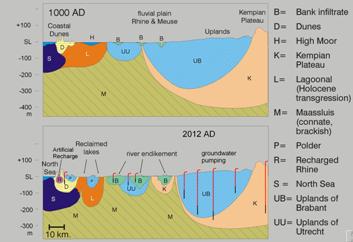
Coastal aquifers are also extremely vulnerable to effects of climate change, especially in delta's and estuaries, due to a combination of sea level rise, land subsidence, increased use of the subsurface in urban areas, and expected higher frequencies of river flood and drought occurrences.
Thus, a systems approach is needed to order the various types of information, to prepare maps showing how past and current distributions of the hydrological and hydrochemical systems, and how water quality evolves along flow lines within the aquifer system.
The Group's systems research aims at the development of tools to: (i) manage and evaluate large hydrochemical data-sets; (ii) map hydrochemical systems and trends in spatial patterns; (iii) establish natural background values of groundwater composition and pollution levels; (iv) derive hydrological system parameters through analytical approaches; and (v) derive hydrological characteristics from hydrochemical data.
These tools are applied to and based on data from various coastal aquifers in the Netherlands, the Eastern Po plain (Italy), Portugal (Aveiro area where the Group's hydrologic field training takes place), and Lebanon.
Current projects
Public water supply well fields in the Netherlands, as a monitoring network to establish natural backgrounds and trends in groundwater quality and aquifer vulnerability.
PhD project: I. (Igor) Mendizabal
Period: 2008-2011
Funding: Joint Research Program of Dutch Waterworks (BTO) and Delft Cluster (project CT 05.30).
Analysis and management of the Damour coastal, dolomitic limestone aquifer, South Beirut, Lebanon.
PhD project: W. (Wisam) Khadra
Period: 2010-2014
Funding: Partial funding by International Navigation Trading and Contracting Co. (INTC), Lebanon.
Pollutant peaking in groundwater catchments for drinking water supply in the NE Netherlands
PhD project: M. (Martin) de Jonge
Period: 2009-2015
Funding: Vitens Water Supply Company.
Effects of gravel pit lakes on the hydrology and hydrochemistry of the surrounding aquifer and river basins
PhD project: P. (Pauline) Mollema
Period: 2011-2015
Funding: This Italian study is partly funded by the City of Ravenna and ENI. WML supports the work in the investigated Dutch gravel pits.
Dynamics of plant ecology and base chemistry in fen and fen meadows in the Netherlands
PhD project: C. (Camiel) Aggenbach
Period: 2005-2011
Funding: Joint Research Program of Dutch Waterworks (BTO).
Sustainable Development and Management of the Shallow Subsurface
PhD project: D. (Derk) van Ree
Period: 2011-2016
Funding: Deltares.
Collaborators
Publications
- Mendizabal, I., P.J. Stuyfzand & P.K. Baggelaar 2012. Hydrochemical trends for public supply well fields in The Netherlands (1898-2008), natural backgrounds and upscaling to groundwater bodies. J. Hydrol. 450-451, 279-292.
- Mendizabal, I., P.J. Stuyfzand & A. Wiersma 2011. Hydrochemical system analysis of public supply well fields, to reveal water-quality patterns and define groundwater bodies: The Netherlands. Hydrogeology Journal 19, 83-100.
- Mendizabal, I. & P.J. Stuyfzand 2011. Quantifying the vulnerability of well fields towards anthropogenic pollution: The Netherlands as an example. J. Hydrology 398, 260-276.
- De Louw P.G.B., G.H.P. Oude Essink, P.J. Stuyfzand, S.E.A.T.M. van der Zee 2010. Upward groundwater flow in boils as the dominant mechanism of salinization in deep polders, The Netherlands. J. Hydrology 394 (2010) 494-506.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. & K.J. Raat 2010. Benefits and hurdles of using brackish groundwater as a drinking water source in the Netherlands. Hydrogeol. J. 18, 117-130.
- Mendizabal, I. & P.J. Stuyfzand 2009. Guidelines for interpreting hydrochemical patterns in data from public supply well fields and their value for natural background groundwater quality determination. J Hydrol. 379 (2009), 151-163.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. & J. Kappelhof. 2005. Floating, high-capacity desalting islands on renewable multi-energy supply. Desalination 177 (2005), 259-266.
- Van der Velde, R.T., P. Hiemstra, E.C.M. Ruijgrok, P.J. Stuyfzand, J.W. Kooiman & G. Mesman 2005. The benefits of air pollution control to water supply in the Netherlands. Water Environment 21, December, 48-50.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. 1999. Patterns in groundwater chemistry reflecting groundwater flow. Hydrogeol. J. 7, Theme issue 'Groundwater as a geologic agent', J. Tóth (ed), Hydrogeology J. (7), 15-27.
- Grootjans, A.P., W.H.O.Ernst & P.J. Stuyfzand 1998. European dune slack ecosystems: wetlands with many endangered species and strong interactions of biology, pedogenesis and hydrology. TREE 13, 96-100.
- Grootjans, A.P., F.P. Sival & P.J. Stuyfzand 1996. Hydro-geochemical analysis of a degraded dune slack. Vegetatio 126, 27-38.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. 1995. The impact of land reclamation on groundwater quality and future drinking water supply in The Netherlands. Water Sci & Technol. 31 (1995), 47-57.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. 1993. Hydrochemistry and hydrology of the coastal dune area of the Western Netherlands. Ph.D Thesis Vrije Univ. Amsterdam, published by KIWA, ISBN 90-74741-01-0, 366 p.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. 1990. Hydrochemical facies analysis of coastal dunes and adjacent low lands: The Netherlands as an example. In "Dunes, European coasts", T.W.M. Bakker, P.D. Jungerius & J.A. Klijn (eds), Catena Supplement 18, 121-132.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. , F. Schaars en K.J. van der Made 2012. Multitracing the origin of brackish and saline groundwaters near a dune catchment area with beach and dune nourishment (Monster, Netherlands). In 'Salt Water Intrusion in Aquifers: Challenges and Perspectives', Proc. SWIM 22, Buzios Brazil.
- Mendizabal, I and P.J. Stuyfzand 2011. HyCA, the all in one approach for efficient spatial and temporal analysis of large water quality databases. Ch.3 in I. Mendizabal 2011, Public supply well fields as a valuable groundwater quality monitoring network, Ph.D thesis VU University Amsterdam, 121p.
- Bonte, M., P.J. Stuyfzand, G. van den Berg, W.A.M. Hijnen 2011. Effects of aquifer thermal energy storage on groundwater quality and the consequences for drinking water production: A case study from the Netherlands. Water Science and Technology 63 (9):1922-1931.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. 2010. Multitracing of artificially recharged Rhine River water in the coastal dune aquifer system of the Western Netherlands. Proc. ISMAR-7, Abu Dhabi, 9-13 Oct 2010.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. & Mendizabal, I. 2010. Trace element concentrations of groundwater from public supply well fields, and their relation with marine sedimentary environments of the aquifer and postdepositional salinity changes. In: M.T. Condesso de Melo et al. (eds), Proceedings SWIM-21 Azores, June 21-26 2010, ISBN 978-972-97711-4-9, p24.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. 2009. Identification, mapping and side reactions of fresh and salt water intrusion in coastal aquifers. Geoitalia 2009, VII Forum Italiano di Scienze della Terra, Rimini, 9-11 settembre 2009, Epitome (3), p.33.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. & R.J. Stuurman 2008. Origin, distribution and chemical mass balances for brackish and saline groundwaters in the Netherlands. Proc. In: G. Barrocu (ed) Proc. 1st SWIM-swica Joint Saltwater Intrusion Conference, Cagliari-Baia de Chia, Sept 24-29 2006, 151-164.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. 2008. Base exchange indices as indicators of salinization or freshening of (coastal) aquifers. In: Program and Proceedings 20th Salt Water Intrusion Meeting, June 23-27 2008, Naples (Fl) USA, Univ Florida, IFAS Research, 262-265.
- Stuyfzand, P.J., P. van Rossum and I. Mendizabal 2008. Does arsenic, in groundwaters of the compound Rhine-Meuse-Scheldt-Ems delta, menace drinking water supply in the Netherlands? In: Arsenic in groundwater, a world problem, Appelo (ed), Proc Seminar Utrecht 29 Nov 2006, Netherlands National Committee IAHS Publ. 5 102-125.
- Stuyfzand P.J., J.W. Kooiman, A. Oosterhof & K.J. Raat 2007. Problems and solutions when recharging brackish aquifers with membrane concentrate from a less brackish groundwater source. In: Management of aquifer recharge for sustainability, P. Fox (ed), Proc. ISMAR-6, 28 Oct-2 Nov 2007, Phoenix AR USA, Acacia Publ. INc., Phoenix, 47-60.
- Stuyfzand, P.J., R.R. Ludwig & P. Kristensen 2007. Impact of climate change on groundwater; a background note for EEA. European Environment Agency.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. 2006. Mapping groundwater bodies with artificial or induced recharge, by determination of their origin and chemical facies. Proc. 5th Intern. Symp. on Management of Aquifer Recharge, ISMAR-5, Berlin 11-16 June 2005, UNESCO IHP-VI, Series on Groundwater No. 13, 839-850.
- Kooiman, J.W., P.J. Stuyfzand, C. Maas & J.W.N.M. Kappelhof 2005. Pumping brackish groundwater to prepare drinking water and keep salinizing wells fresh. In: Groundwater and saline intrusion, selected papers from the 18th SWIM, Cartagena 2004, L. Araguas, E. Custodio & M. Manzano (eds), Publ. Inst. Geol. Y Minero de Espana, Serie Hidrogeologica y aguas subterraneas No.15, 625-635.
- Stuyfzand, P.J., W.J. De Lange & A. Zindler 2005. Recognition, dating and genesis of fresh and brackish groundwaters in the Hollandsch Diep estuary in the compound Rhine-Meuse delta. In: Groundwater and saline intrusion, selected papers from the 18th SWIM, Cartagena 2004, L. Araguas, E. Custodio & M. Manzano (eds), Publ. Inst. Geol. Y Minero de Espana, Serie Hidrogeologica y aguas subterraneas No.15, 665-678.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. 1998. Decalcification and acidification of coastal dune sands in the Netherlands. Water-Rock Interaction, Proc. 9th Intern. Symp. on WRI, Taupo New Zealand, G.B. Arehart & J.R. Hulston (eds), Balkema, 79-82.
- Sival, F.P., A.P. Grootjans, P.J. Stuyfzand & T. Verschoore de la Houssaye 1997. Variation in groundwater composition and decalcification depth in a dune slack: effects on basiphilous vegetation. J. Coastal Conservation 3, 79-86.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. 1996b. The geohydrochemical approach in optimizing groundwater quality monitoring. Proc. 'Monitoring tailor-made II' (Ottens et al., eds), Intern. Work-shop Nunspeet (Neth.) September 1996, 415-419.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. 1996a. Salinization of drinking water in the Netherlands: anamnesis, diagnosis and remediation. SGU Rapporter och Meddelander 87, Proc. 14th SWIM, 17-21 June 1996, Malmö, Geol. Survey Sweden, Uppsala, 168-177.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. 1995. The geohydrochemical approach in optimizing groundwater quality monitoring. Poster presented at 19th IWSA Symposium, September 9-15, Durban (SA), and at workshop 'Monitoring Tailor-made II', Sept. 9-12, 1996, Nunspeet, the Neth.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. & R.J. Stuurman 1994. Recognition and genesis of various brackish to hypersaline groundwaters in The Netherlands. Proc. 13th Salt Water Intrusion Meeting, June 1994, Cagliari Italy, G. Barrocu (ed), Univ. Cagliari, Fac. Engineering, 125-136; also Kiwa-rap-port SWI-95.133, 12p.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. & G.A. Bruggeman 1994. Analytical approximations for fresh water lenses in coastal dunes. Proc. 13th Salt Water Intrusion Meeting, June 1994, Cagliari Italy, G. Barrocu (ed), Univ. Cagliari, Fac. Engineering, 15-33; tevens Kiwa-rapport SWI-95.134, 19p.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. 1994. Advanced mapping of groundwater quality as an aid in designing monitoring programs and selecting areas for superprotection. Proc. Intern. Conf. "Living with Water", Amsterdam 26-29 Sept. 1994, 773-774.
- Lammerts, E.V., A. Grootjans, P.J. Stuyfzand & F. Sival, 1993. Endangered dune slack plants; gastronomers in need of mineral water. Proc. 4th EUCC Congress, Marathon (Greece) 1993, in Coastal Management and Habitat Protection 1, 355-369.
- Bakker, T.W.M & P.J. Stuyfzand, 1993. Nature conservation and extraction of drinking water in coastal dunes : the Meijendel dunes. In : Landscape ecology of a stressed environment, C.C. Vos & P. Opdam (eds), IALE-Studies in Landscape Ecology 1, Chapman & Hall, Lon-don, 244-262.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. 1993. Behaviour of major and trace constituents in fresh and salt intrusion waters, in the Western Netherlands. In Study and modelling of saltwater intrusion into aquifers, E. Custodio & A. Galofré (eds), Proc. 12th Salt Water Intrusion Meeting, November 1992 Barcelona, CIHS. CIMNE Barcelona, 143-160.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. 1991. Nonpoint sources of trace elements in potable groundwaters in The Netherlands. Proc. 18th Int. Water Supply Congress and Exhibition (IWSA) Copenhagen, 25-31 may 1991, Water Supply 9, SS10-11 -SS10-15.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. 1989c. Factors controlling trace element levels in ground water in The Netherlands. Proc. Sixth Int. Symp. Water Rock Interaction, Malvern (UK), August 3-8 1989, D.L. Miles (ed), Balkema Rotterdam, 655-659.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. 1989b. A new hydrochemical classification of watertypes. IAHS Publ. 182, 89-98.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. 1989a. Hydrochemical evidence of fresh and salt water intrusions in the coastal dunes aquifer system of the Western Netherlands. (Flemish) Natuurwe-tensch. Tijdsch. 70, 9-29.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. 1987. Effects of vegetation and air pollution on groundwater quality in calcareous coastal dunes near Castricum, the Netherlands: Lysimetric observations. Proc. Intern. Symp on Acidification and water pathways, Bolkesjo Norway 4-8 may 1987, Norw. Nat. Comm. for Hydrol. (ed), vol.2 , 115-125.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. 1986. A new hydrochemical classification of water types : principles and application to the coastal dunes aquifer system of the Netherlands. Proc. 9th Salt Water Intrusion Meeting, Delft 12-16 may, Delft Univ. Techn., 641-655. Also published in Hydrogeology of salt water intrusion; a selection of SWIM papers, W. de Breuck (Ed), Intern. Contrib. to Hydrogeology (11), Verlag Heinz Heise, 329-343.
- Stuyfzand, P.J. 1984. Groundwater quality evolution in the upper aquifer of the coastal dune area of the western Netherlands, IAHS Publ. 150, 87-98.
Last modified: Mon Dec 28 14:55:41 CET 2015